
This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. These cookies ensure basic functionalities and security features of the website, anonymously. Necessary cookies are absolutely essential for the website to function properly. It is found that under the same temperature and pressure, equal volumes of all gases contain the same number of particles. However, this cannot be done for solids and liquids. How are the number of moles of a gas determined?Ĭhemists determine the number of moles of any gas by measuring its volume. V = n ⋅ V molar For 2 moles of a gas at STP the volume will be 2 moles ⋅ 22.4 L/mol = 44.8 L


So, if you are given these values for temperature and pressure, the volume occupied by any number of moles of an ideal gas can be easily derived from knowing that 1 mole occupies 22.4 L. The most common example is the molar volume of a gas at STP (Standard Temperature and Pressure), which is equal to 22.4 L for 1 mole of any ideal gas at a temperature equal to 273.15 K and a pressure equal to 1.00 atm. Which is an example of molar volume of a gas? STP = 1 atm of pressure and 273 K for temperature P = 1 atm Using the Ideal Gas Law, you would find the volume of 1 mole of a gas at Standard Temperature and Pressure (STP).
#ARGON MOLAR MASS HOW TO#
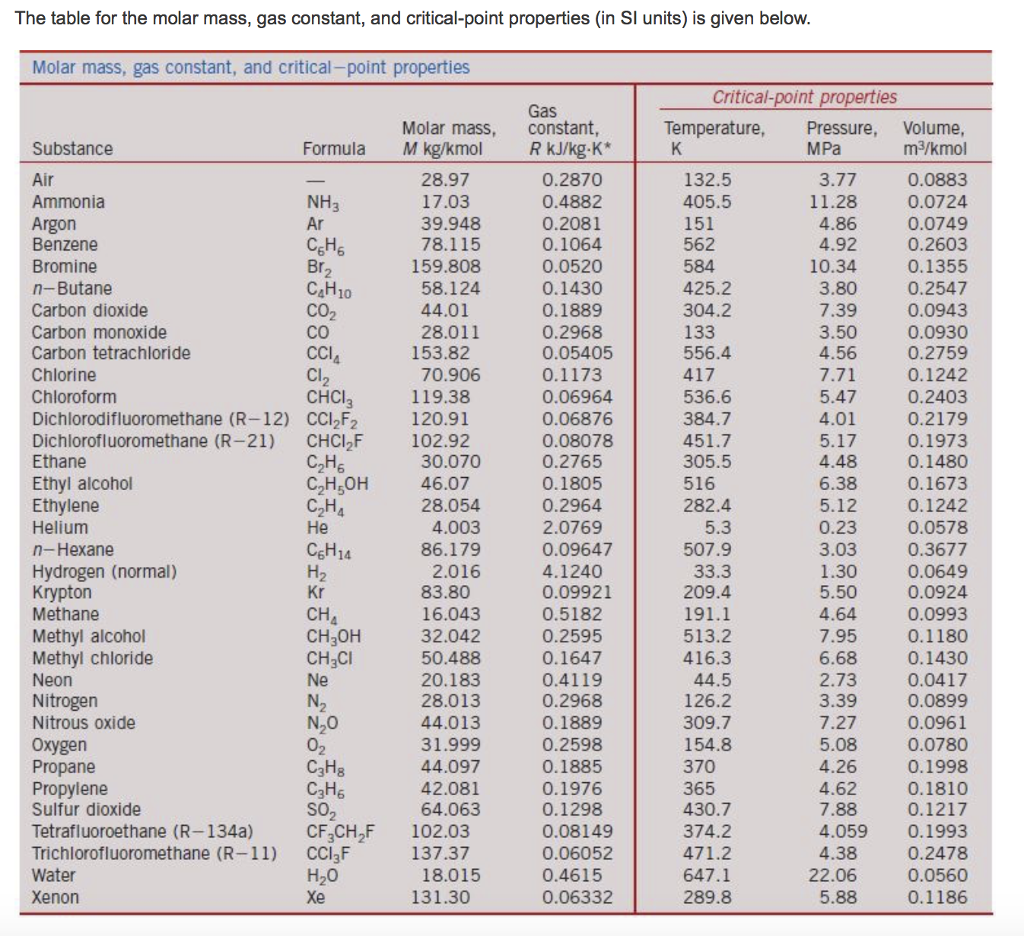
Remember the conversion factor will be different at STP and SATP! How to calculate molar volume of a gas at STP? This can be used as a conversion factor just like molar mass! At STP, one mole of gas has a volume of 22.4 L, which is approximately the volume of 11 “empty” 2 L pop bottles. What is the molar volume at STP and SATP? EXAMPLE: A gas sample occupies a volume of 125 mL at STP. Notice: the second value of the variable is the first value multiplied by fractions of the other two variables. What is the volume of your gas sample at STP?Īt STP one mole of any gas occupies a volume of 22.4 L: this is the molar volume. This, 22.4 L, is probably the most remembered and least useful number in chemistry. So, the volume of an ideal gas is 22.41 L/mol at STP. This makes for a very useful approximation: any gas at STP has a volume of 22.4 L per mole of gas that is, the molar volume at STP is 22.4 L/mol (Figure 6.3 “Molar Volume”). At STP, gases have a volume of 22.4 L per mole. Standard temperature and pressure (STP) are a useful set of benchmark conditions to compare other properties of gases. What is the volume of these gases at STP? “P” is pressure, “V” is volume, n is the number of moles of a gas, “R” is the molar gas constant and “T” is temperature. Molar gas volume is one mole of any gas at a specific temperature and pressure has a fixed volume. It can be calculated by dividing the molar mass (M) by mass density (ρ). How do you find the molar volume of a gas at STP?Īt standard Temperature and Pressure (STP) the molar volume (Vm) is the volume occupied by one mole of a chemical element or a chemical compound. So, the volume occupied by 56.5 g of Ar at STP is 31.7 L.

The volume of 1 mol of an ideal gas at STP is 22.4 L. What is the molar volume of argon gas at STP? 7 How to calculate the volume of a mole?.6 How to calculate molar volume of a gas at STP?.5 What is the volume of your gas sample at STP?.1 What is the molar volume of argon gas at STP?.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
